A guide to fixing some common issues with k6 Cloud.
Prefer local debugging
Debugging helps ensure your code produces the expected results. While the script editor can catch some errors, it has limited debugging abilities.
Instead, aim to debug your k6 scripts on your local machine. Local debugging avoids problems that would come up on k6 Cloud:
- A cloud test counts against any subscription limits you have.
- Execution is slower when streaming or executing in the cloud. We want debugging to be a fast iterative process.
If you configure Virtual Users or duration in your script, you can override the values with CLI flags.
Tests with 1 iteration with 1 Virtual User are quicker and can make the debugging easier.
For debugging, k6 also provides a few builtin options:
--http-debug prints all the requests and responses to the console.
Read more about HTTP debugging.
Console logging methods can print any message to the console. k6 Cloud shows console logs on the Logs Tab.
You can also use the --console-output option to redirect console logs to an output file.
Invited to an organization but can't run tests
I was invited to an organization with a subscription. However, When I try to run tests, I get an error that my subscription doesn't have enough Virtual Users/exceeds the duration/uses too many load zones. Our subscription allows for the test I want to run. What is wrong and how do I fix this?
If you encounter a similar situation, the problem is probably that you run the test from a different organization with another subscription.
This situation often happens because when you register your account, as the k6 Cloud automatically creates a "personal" default organization for you. In this case, you might have two organizations: your "personal" organization and the invited organization.
By default, tests run from your "personal" organization.
How do I change the organization to fix this?
If you run tests from the web interface, use the user menu to select a project within the desired organization.
If you run tests from the k6 CLI, set the projectID in the test script.
- Copy the project ID from the top-left corner of the project dashboard.
- Set the projectID as a cloud execution option.
Read more about managing Organizations and Projects.
Open a firewall for k6 Cloud
k6 Cloud tests are dynamically allocated from our cloud providers. k6 doesn't know the source IP until the test is running.
To open your firewall to k6 cloud traffic, you have multiple options.
Open up your firewall to the whole range of AWS IP addresses used by the load zones where you want to run your load test from. We list the full range of IPs.
Use HTTP headers, URL query parameters, or unique data that identifies the traffic as belonging to your load test. This requires that your firewall supports scanning application payload data and can apply rules based on what it finds.
Custom HTTP headers
You need to add the header to every single request.
Custom user agent
If your VUs don't need to have a certain user agent, you can use the userAgent option to set the "User-Agent" header for all subsequent requests. That header could contain your token value, and you wouldn't have to modify every HTTP request in your script.
In this example, the user agent is set to MyK6UserAgentString/1.0
Query parameters
Query parameters are another option (as long as they won't interfere with your application functionality):
A custom hostname
Another option would be to request content from a hostname that is not in the DNS. Your site would need to be configured to respond to requests for that hostname, though.
Here's how to do it from the k6 Cloud side:
This last solution requires that your firewall terminates SSL traffic. Otherwise it won't see the Host header in unencrypted form. You could also use unencrypted HTTP, but get a bit less security.
Max concurrency reached error
Concurrency
In the context of the k6 Cloud, concurrency is the ability to execute more than one test run simultaneously.
Your k6 Cloud subscription defines the maximum number of concurrent test runs. If you need to increase this limit, contact our support team.
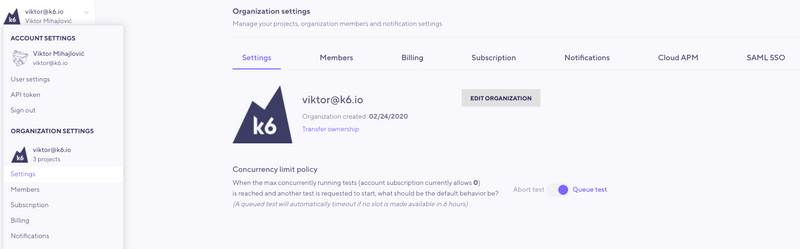
Additionally, you can change the concurrency limit policy that defines how k6 Cloud acts when the organization reaches the limit and a new test run is triggered. Two options are available:
- Queue test: the new test run will be queued for execution and started once a slot is opened. A queued test will timeout if no slot is available in 6 hours. This is the current default option.
- Abort test: the new test run will be automatically aborted.
Changes to the default concurrency policy
On January 31st, 2023, the default concurrency policy changed from Abort test to Queue test. To avoid confusion, k6 kept the old default for organizations who joined before the change.
If your organization uses the old default and wants to upgrade to Queue test policy, change the policy as described in the following section.
Changing the concurrency limit policy
To change the concurrency limit policy, you must be the organization owner. You can change the policy in your user menu, at Organization settings > Settings:
Data uploads with k6 Cloud
The test builder and script editor in the k6 Cloud don't support uploading data files in your test.
To execute a cloud test that uploads a data file, run the tests from the CLI and follow the steps described on the data uploads example.